- Home
- ABOUT DR. YANNI
- SPINE DISORDERS
- General Information
- Anatomy of the Spine
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Bone Grafts
- Back and Neck Braces
- Diagnosing Spine Problems
- Epidural Steroid Injection (ESI)
- Osteoporosis
- Lifestyle Risk Factors
- Biological and Medical Risk Factors
- Preventive Treatment Options
- Possible Complications of Spine Surgery
- Pain Medications
- Post Surgery Rehabilitation
- Surgical After Care
- Spinal Injections
- Spinal Rehabilitation
- Radiological Imaging and Tests
- Cervical Spine
- Anterior Cervical Fusion
- Anatomy of the Cervical Spine
- Cervical Corpectomy and Strut Graft
- Cervical Fusion
- Cervical Kyphosis
- Cervical Laminectomy
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Cervical Spinal Stenosis
- Neck Pain (Overview)
- Posterior Cervical Fusion
- Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Cervical Spine
- Rehabilitation of the Cervical Spine
- Artificial Disc
- Thoracic Spine
- Lumbar Spine
- Adult Scoliosis
- Compression Fractures
- Degenerative Adult Scoliosis
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Intervertebral Cages
- Low Back Pain (Overview)
- Low Back Pain in Athletes
- Laminotomy and Discectomy
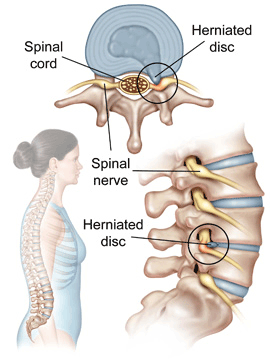
- Lumbar Herniated Disc
- Lumbar Laminectomy
- Lumbar Spine Anatomy
- Lumbar Spinal Fusion
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Lumbar Spine Surgery
- Possible Complications
- Pedicle Screws and Rods
- Rehabilitation for Low Back Pain
- Scoliosis
- Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome
- General Information
- For Patients
- Referring Physicians
- Practice Information
- Contact Us
- QUESTIONS? CALL US: (949) 515-0051
×
- Home
- ABOUT DR. YANNI
- SPINE DISORDERS
- General Information
- Anatomy of the Spine
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Bone Grafts
- Back and Neck Braces
- Diagnosing Spine Problems
- Epidural Steroid Injection (ESI)
- Osteoporosis
- Lifestyle Risk Factors
- Biological and Medical Risk Factors
- Preventive Treatment Options
- Possible Complications of Spine Surgery
- Pain Medications
- Post Surgery Rehabilitation
- Surgical After Care
- Spinal Injections
- Spinal Rehabilitation
- Radiological Imaging and Tests
- Cervical Spine
- Anterior Cervical Fusion
- Anatomy of the Cervical Spine
- Cervical Corpectomy and Strut Graft
- Cervical Fusion
- Cervical Kyphosis
- Cervical Laminectomy
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Cervical Spinal Stenosis
- Neck Pain (Overview)
- Posterior Cervical Fusion
- Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Cervical Spine
- Rehabilitation of the Cervical Spine
- Artificial Disc
- Thoracic Spine
- Lumbar Spine
- Adult Scoliosis
- Compression Fractures
- Degenerative Adult Scoliosis
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Intervertebral Cages
- Low Back Pain (Overview)
- Low Back Pain in Athletes
- Laminotomy and Discectomy
- Lumbar Herniated Disc
- Lumbar Laminectomy
- Lumbar Spine Anatomy
- Lumbar Spinal Fusion
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Lumbar Spine Surgery
- Possible Complications
- Pedicle Screws and Rods
- Rehabilitation for Low Back Pain
- Scoliosis
- Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome
- General Information
- For Patients
- Referring Physicians
- Practice Information
- Contact Us